Image Reconstruction Algorithms and Deep Learning
As MRI data are not acquired from image space, but from 2D Fourier space (k-space), a reconstruction step is required to transform sampled data in the k-space to the image space in order to obtain MR images. Manipulation of how data points sampled in the k-space will affect the speed of data acquisition and the quality of reconstructed images. In practice, one would apply undersampling to speed up data acquisition. This is particular important in clinical diagnostics because one would like to reduce patient scan time and motion artefacts. However, undersampling in k-space would lead to Nyquist aliasing in image space. This problem may be cleverly alleviated by advanced reconstruction techniques such as parallel imaging.
One recent research in our lab is the investigation of a novel way to provide simultaneous multislice (SMS) echo-planar imaging (EPI) reconstruction with k‐space implementation and robust Nyquist ghost correction. EPI has been widely used in many MRI applications, especially functional MRI for its ultrafast imaging capability. We proposed a PEC‐GRAPPA approach as shown below.
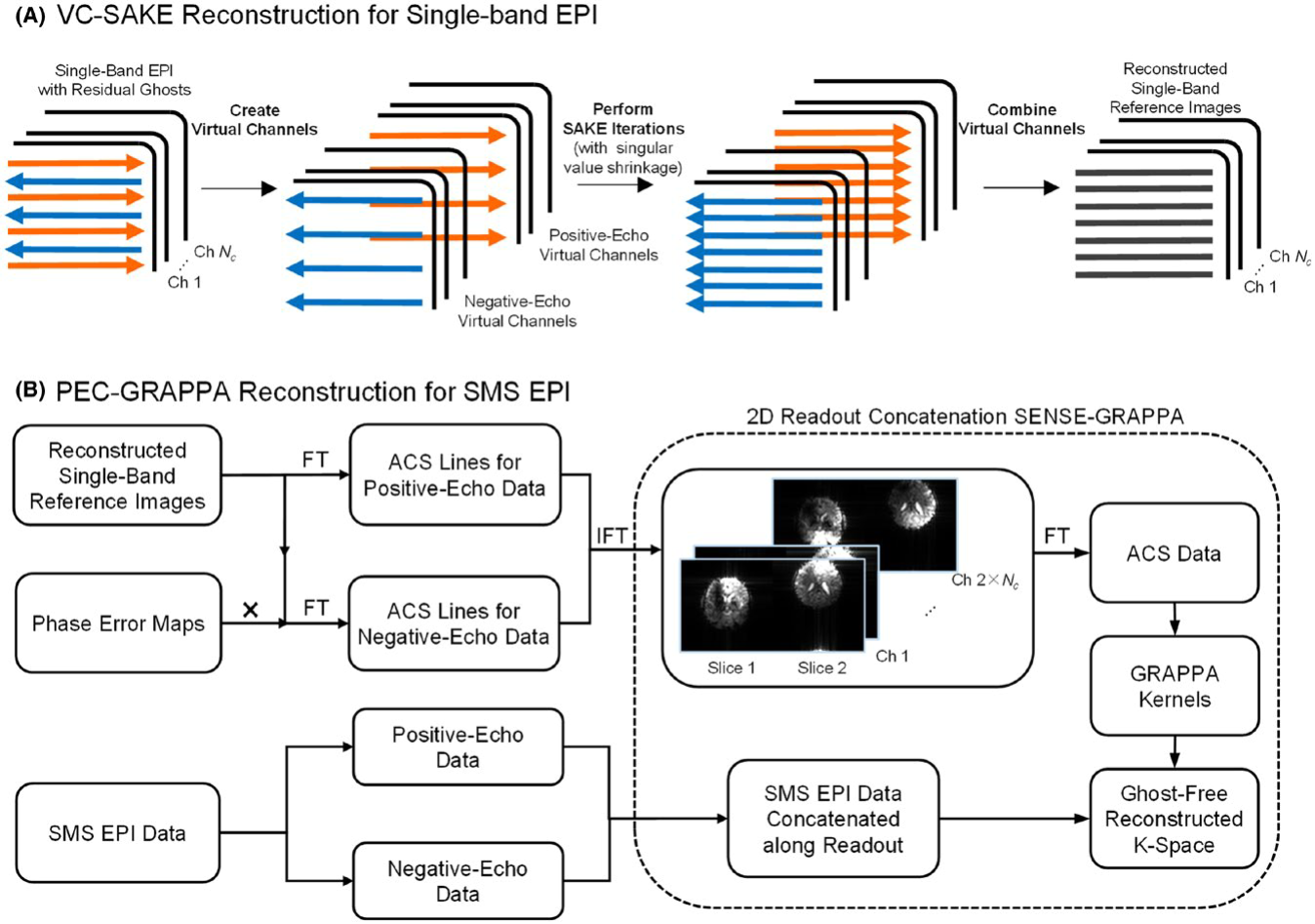
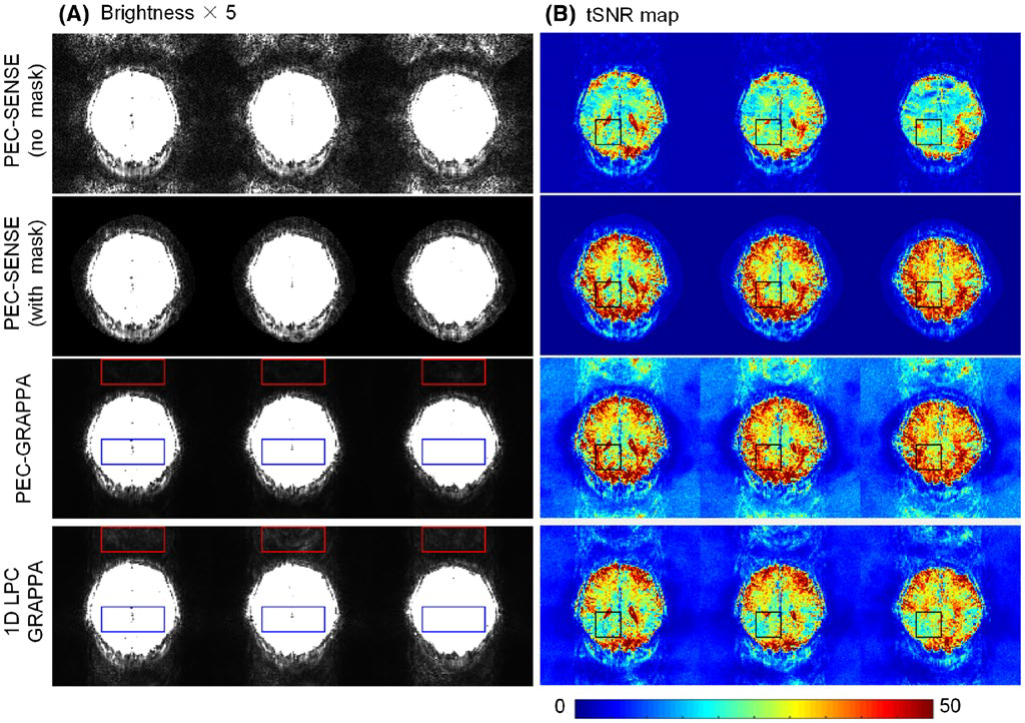
The proposed approach was able to robustly reconstruct SMS EPI images from 7T phantom and human brain data, effectively removing the phase error‐induced artefacts in SMS EPI scan without significant and laborious tuning. The artefact level and temporal signal-to-noise ratio (tSNR) are comparable to those of PEC‐SENSE with masking.